AllocInit
从上面两种创建对象的方法可以看出第一种方式对象的创建是在 alloc 中,init 方法只是返回已经创建的对象。通过 new 方法创建的对象本质还是 alloc 和 init 的结合。
创建对象的两种方法
[[Class alloc] init]
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
// Base class implementation of +alloc. cls is not nil.
// Calls [cls allocWithZone:nil].
id_objc_rootAlloc(Class cls){
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}
// Replaced by CF (throws an NSException)
+ (id)init {
return (id)self;
}
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id_objc_rootInit(id obj){
// In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function.
// Many classes do not properly chain -init calls.
return obj;
}
[Class new]
+ (id)new {
return [callAlloc(self, false/*checkNil*/) init];
}
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
从上面两种创建对象的方法可以看出第一种方式对象的创建是在 alloc 中,init 方法只是返回已经创建的对象。通过 new 方法创建的对象本质还是 alloc 和 init 的结合。
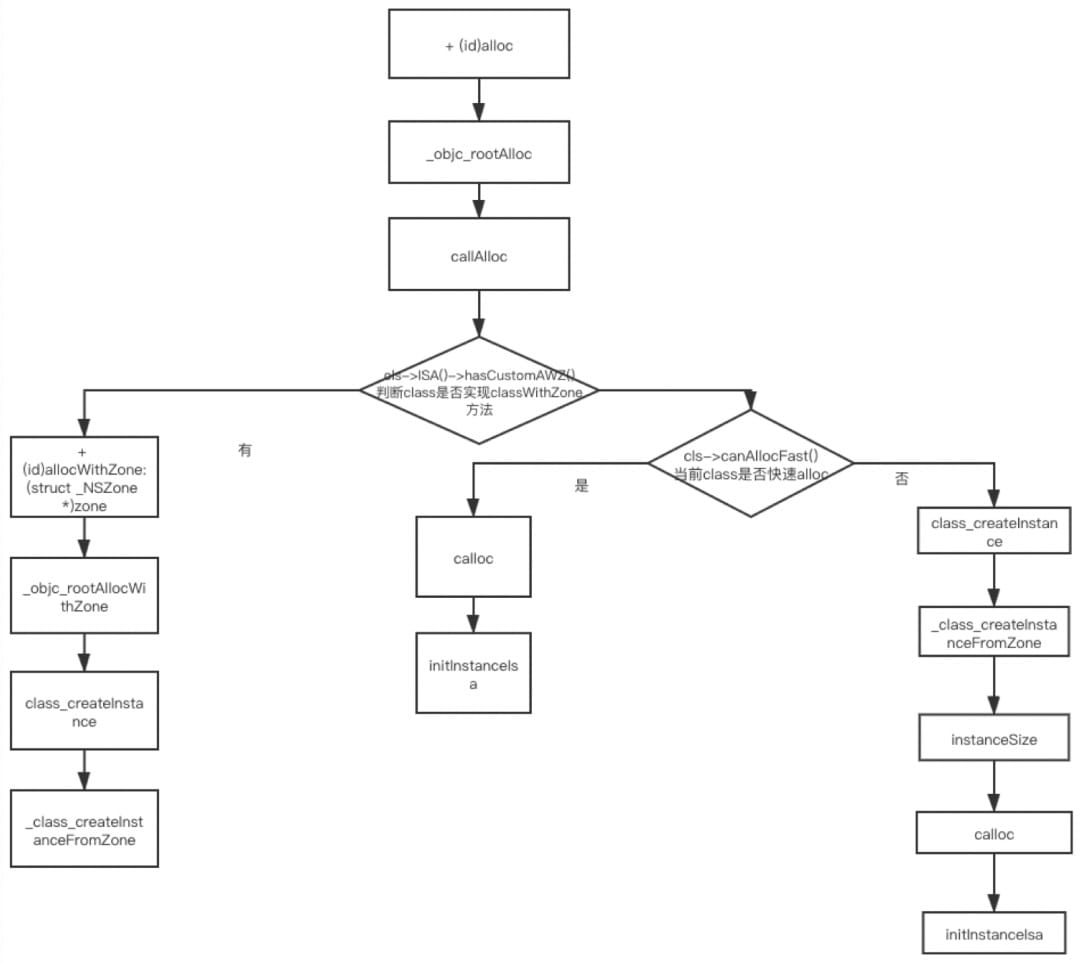
callAlloc
// Call [cls alloc] or [cls allocWithZone:nil], with appropriate
// shortcutting optimizations.
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
{
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
#if __OBJC2__
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {
// No alloc/allocWithZone implementation. Go straight to the allocator.
// fixme store hasCustomAWZ in the non-meta class and
// add it to canAllocFast's summary
if (fastpath(cls->canAllocFast())) {
// No ctors, raw isa, etc. Go straight to the metal.
bool dtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
id obj = (id)calloc(1, cls->bits.fastInstanceSize());
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, dtor);
return obj;
}
else {
// Has ctor or raw isa or something. Use the slower path.
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) return [cls allocWithZone:nil];
return [cls alloc];
}
slowpath 和 fastpath
// 表示 x 的值为真的可能性更大
#define fastpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1))
// 表示 x 的值为假的可能性更大
#define slowpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 0))
__builtin_expect 是 GCC 提供给程序员使用,目的是将 “分支转移” 的信息提供给编译器,这样编译器可以对代码进行优化,以减少指令跳转带来的性能下降。
其实代码中的 slowpath 和 fastpath 删除后并不会影响这段代码的功能, slowpath 和 fastpath 的添加就是为了告诉编译器 if 条件语句中是大概率事件还是小概率事件,从而让编译器对代码进行优化。
代码中,if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil; 就是说明 cls 大概率是有值的,告诉编译器编译时优化,下面就到了 cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ()。
hasCustomAWZ
asCustomAWZ 作用是判断当前类有没有实现 allocWithZone 方法。它是通过类的结构体 objc_class 中的 hasCustomAWZ 方法判断的:
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
bool hasCustomAWZ() {
return ! bits.hasDefaultAWZ();
}
hasDefaultAWZ() 的方法实现如下:
#else
bool hasDefaultAWZ() {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ;
}
void setHasDefaultAWZ() {
data()->setFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
void setHasCustomAWZ() {
data()->clearFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
#endif
RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ 是用来标记用户有没有自己实现 allocWithZone 方法。由于类是有懒加载的概念的,所以第一次给该类发送消息之前,该类是没有加载的,因此当类收到 alloc 消息的时候,进入到 hasCustomAWZ 时并没有默认实现 allocWithZone 方法,所以 hasCustomAWZ 返回 true,因此会直接进入到 [cls alloc]。当再次调用 callAlloc 时候 DefaultAWZ 为 ture,hasCustoAWZ 为 false 这样会进入到下一个流程。
canAllocFast
canAllocFast 作用是判断当前类是否可以快速开辟内存,需要注意的是这里永远不会调用,因为 canAllocFast 内部返回的是 false。具体实现如下:
bool canAllocFast() {
assert(!isFuture());
return bits.canAllocFast();
}
bool canAllocFast() {
return false;
}
可以看到 canAllocFast 返回 False, 于是来到了下一流程:class_createInstance。
class_createInstance
id class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes){
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, extraBytes, nil);
}
static __attribute__((always_inline))id_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,bool cxxConstruct = true,size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil){
if (!cls) return nil;
assert(cls->isRealized()); // Read class's info bits all at once for performance bool hasCxxCtor = cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer(); //!! 是否可以创建NonPointer
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
id obj;
if (!zone && fast) {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
} else {
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc ((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (!obj) return nil;
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
if (cxxConstruct && hasCxxCtor) {
obj = _objc_constructOrFree(obj, cls);
}
return obj;
}
hasCxxtor() 和 hasCxxDtor
在这里开始创建对象分配内存空间,hasCxxtor() 和 hasCxxDtor() 是用来处理 C++ 成员变量的构造和析构的, hasCxxtor 是判断当前 class 或者 superclass 是否有. cxx_construct 的实现, hasCxxDtor 是用来判断当前 class 或者 superclass 是否有. cxx_destruct 的实现, canAllocNonpointer 是判断是否可以创建 Nonpointer。